
What Is RAG and Why Does It Matter for Document Analysis?
RAG, which stands for Retrieval Augmented Generation, is a method that grounds AI-generated answers in actual source documents rather than relying on general knowledge that may be outdated, incomplete, or entirely fabricated. It represents a fundamental shift in how AI systems process and respond to questions about specific information contained within user-provided files.
Rather than being a simple chatbot feature, RAG encompasses a systematic approach that includes document ingestion, text chunking, vector embedding, semantic search, and context-aware generation. Every professional who works with documents, from financial analysts reviewing quarterly reports to legal teams examining contracts, or institutions analyzing sensitive and lenghty files, benefits from understanding how RAG transforms raw files into queryable knowledge bases.
Understanding RAG is essential for business professionals, researchers, legal practitioners, and analysts because standard AI chatbots generate responses based on patterns learned during training. When you ask about specific information in your documents, these systems often produce confident but incorrect answers. This phenomenon, known as hallucination, creates serious risks when decisions depend on accurate information extraction.
RAG eliminates hallucination by adding a retrieval step before generation. The system first searches your documents for relevant sections, then generates answers based exclusively on what it found. The result is responses grounded in your source material with citations pointing to specific passages rather than invented content.
How Does the RAG Process Work?
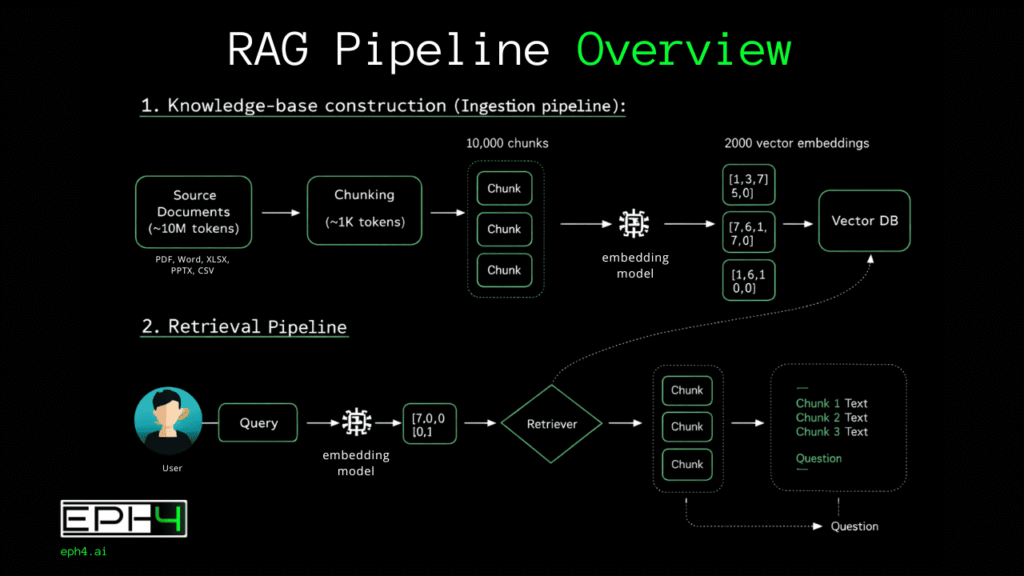
The RAG process is divided into distinct phases, each serving a specific function in transforming static documents into interactive knowledge sources.
- The Ingestion Phase involves uploading documents and preparing them for intelligent search. The system accepts multiple file formats and processes each according to its structure, extracting text while preserving contextual relationships between sections, headings, tables, and paragraphs.
- The Chunking Phase breaks documents into smaller segments optimized for search and retrieval. Chunk size balances granularity against context preservation. Segments that are too small lose meaning while segments that are too large reduce search precision. Proper chunking ensures relevant information can be isolated without losing surrounding context.
- The Embedding Phase converts text chunks into numerical vector representations that capture semantic meaning. These vectors enable the system to understand relationships between concepts rather than matching only exact keywords. Documents discussing revenue growth and financial performance are recognized as related even when using different terminology.
- The Retrieval Phase activates when you ask a question. Your query is converted into the same vector space as your documents, and the system identifies chunks with the highest semantic similarity. This surfaces relevant passages regardless of whether they contain your exact words.
- The Generation Phase sends retrieved chunks along with your question to the language model. The AI generates responses using only the provided context, citing specific sections and acknowledging when information is not present in the source material.
Together, these phases create a system that answers questions with documented accuracy rather than probabilistic guessing.
What Is the Difference Between Standard AI Chat and RAG Systems?
Standard AI chat and RAG systems serve fundamentally different purposes based on whether users need general knowledge or document-specific accuracy.
Standard AI chat relies entirely on knowledge encoded during model training. The system generates responses by predicting likely word sequences based on patterns learned from training data. It cannot access information created after its training cutoff, cannot read documents you possess, and cannot verify whether its responses match any authoritative source. When asked about specific content in your files, standard chat either refuses to answer or generates plausible-sounding text that may be completely fabricated.
RAG systems separate knowledge storage from reasoning capability. Your documents become the authoritative source, and the AI serves as an intelligent interface for querying that source. The system cannot hallucinate information that does not exist in your files because generation is constrained to retrieved context. When information is absent, the system acknowledges the gap rather than inventing content.
The choice between standard chat and RAG depends entirely on whether you need general conversation or documented accuracy. Research, analysis, legal review, financial examination, and any task requiring verifiable answers demands RAG architecture. Standard chat suffices for creative brainstorming, general questions, and tasks where factual precision is not critical.
How Does EPH4 Implement RAG Without Requiring Accounts?
EPH4 replaces traditional account systems with access keys that provide full functionality while maintaining complete user privacy.
The access key system generates unique identifiers instantly without collecting personal information. No email address, no password, no identity verification. The key grants access to a defined session with specific resource allocations including document upload limits, question quotas, and time boundaries.
Session isolation ensures each access key operates independently. Documents uploaded under one key are invisible to other sessions. No cross-contamination of data occurs between users, and no persistent user profiles accumulate over time.
Automatic deletion activates when sessions expire. The system purges all associated data including uploaded files, generated embeddings, question history, and response logs. This deletion is architectural, not policy-based. The system lacks capability to retain data beyond session boundaries because retention infrastructure does not exist.
Resource allocation for free access keys includes three sessions total, limited document uploads per session, limited questions per session, and reduced time session duration. These limits enable meaningful evaluation while maintaining system sustainability.
This approach delivers full RAG capability without the privacy compromises inherent in account-based systems. Users evaluate the technology on its merits rather than surrendering personal information for access.
What Document Formats Does EPH4 Support?
EPH4 supports five document formats that encompass the files professionals actually work with daily, extending beyond the PDF-only limitation common in competing tools.
- PDF support handles reports, research papers, contracts, manuals, and any document distributed in portable document format. The system extracts text while preserving structural relationships between sections, enabling accurate retrieval from complex multi-section documents.
- Word document support processes business documents, proposals, drafts, and collaborative files in .docx format. Formatting, headings, and document structure inform the chunking process to maintain contextual integrity.
- Excel spreadsheet support enables querying tabular data, financial models, lists, and structured datasets in .xlsx format. The system understands row and column relationships, enabling questions about specific data points, ranges, and calculated values.
- CSV support handles data exports, database extracts, logs, and any comma-separated dataset. This format bridges the gap between database systems and document analysis, allowing RAG queries against structured data sources.
- PowerPoint support processes presentations, slide decks, and visual documents in .pptx format. Content from slides, speaker notes, and embedded text becomes queryable through the same natural language interface.
Multi-document querying allows uploading multiple files and asking questions that span across all of them simultaneously. The system retrieves relevant sections from whichever documents contain pertinent information, enabling comparative analysis and cross-reference queries that would require hours of manual review.
What Visualization Capabilities Does EPH4 Provide?
Beyond text-based answers, EPH4 automatically generates data visualizations when queries involve numerical information, trends, comparisons, or any content suitable for graphical representation.
Automatic chart suggestion analyzes query results and identifies when visualization would enhance understanding. Questions about financial trends, comparative metrics, distribution patterns, or temporal changes trigger chart recommendations without requiring manual specification.
Nineteen chart types provide appropriate visualization options for different data characteristics. Bar charts display categorical comparisons. Line charts reveal trends over time. Pie charts show composition breakdowns. Scatter plots expose correlations. Radar charts compare multiple variables simultaneously. Heatmaps visualize density and concentration patterns. Specialized chart types address specific analytical needs including waterfall charts for cumulative effects and funnel charts for process stages. (Full access of features only in Workspaces)
Direct generation from document data eliminates the traditional workflow of extracting information, transferring to spreadsheet software, formatting data, and creating charts manually. The system generates visualizations directly from retrieved document content, reducing hours of work to seconds.
This capability transforms RAG from a question-answering tool into a document analysis platform. Users extract insights and communicate findings visually without switching applications or performing manual data manipulation.
How Does EPH4 Compare to Other Document AI Tools?
EPH4 differentiates from competing document AI tools across several dimensions that matter for professional users evaluating options.
Registration requirements vary significantly across platforms. EPH4 requires no registration whatsoever. ChatPDF offers limited functionality without accounts but restricts features for unregistered users. AskYourPDF and PDF.ai require full account creation before any usage. This distinction matters for users who need immediate access without administrative overhead or privacy exposure.
Format support reveals substantial differences in versatility. EPH4 handles PDF, Word, Excel, CSV, and PowerPoint files. Most competitors support only PDF, requiring users to convert other formats before analysis. This limitation adds friction and potentially loses formatting information during conversion.
Visualization capability exists exclusively in EPH4 among free document AI tools. No competing platform automatically generates charts from document analysis. Users of other tools must export findings and create visualizations separately.
Multi-document querying availability differs between free and paid tiers across platforms. EPH4 provides cross-document analysis in free access. ChatPDF and AskYourPDF restrict this capability to paid subscriptions.
Data retention policies range from indefinite storage to automatic deletion. EPH4 purges all data when sessions expire. Several competitors retain documents and usage data without clear deletion timelines, raising privacy concerns for sensitive materials.
Who Benefits Most from RAG Document Analysis?
Different professional contexts derive distinct value from RAG capabilities based on their document analysis requirements and accuracy demands.
Financial analysts and business professionals process quarterly reports, annual filings, market research, and competitive intelligence documents. RAG enables extracting specific metrics from lengthy reports, comparing performance across multiple documents, and generating visualization-ready insights for stakeholder presentations. Questions that previously required hours of manual searching resolve in seconds with documented source citations.
Legal and compliance professionals review contracts, regulatory filings, policy documents, and case materials. RAG supports searching across multiple agreements for specific clauses, comparing terms between document versions, extracting obligations and deadlines, and summarizing regulatory requirements. The citation capability proves particularly valuable when findings must be verified and documented.
Government agencies, NGOs, and institutional organizations process policy documents, regulatory filings, grant applications, audit reports, and compliance materials that often span hundreds of pages across multiple departments. RAG enables rapid extraction of specific provisions from lengthy legislative texts, cross-referencing requirements across regulatory frameworks, and synthesizing findings from extensive institutional records. The ephemeral architecture of EPH4 proves critical for these users because sensitive citizen data, classified policy discussions, and confidential operational documents cannot risk exposure through indefinite third-party storage. Session-based processing ensures institutional materials never persist beyond immediate analysis needs.
Academic researchers and students analyze research papers, textbooks, literature reviews, and source materials. RAG accelerates literature review by enabling comparative questions across multiple papers, extracting methodological details without reading entire documents, and synthesizing findings from dozens of sources. The accuracy grounding reduces risk of misattributing or misrepresenting source material.
Small business owners who lack dedicated analyst teams use RAG for quick insights from financial statements, contract review before signing agreements, competitive intelligence from market reports, and data visualization for board presentations. The no-account model proves particularly valuable for occasional users who need capability without ongoing subscription commitments.
What Privacy and Security Protections Does EPH4 Provide?
EPH4 implements privacy protection through architectural design rather than policy promises, ensuring user data cannot be retained, shared, or exploited regardless of future business decisions.
Ephemeral architecture means the system lacks infrastructure for persistent data storage. Session data exists only in temporary processing memory. When sessions terminate, automatic purging removes all traces including documents, embeddings, query logs, and response history. No backups exist. No archives accumulate. No recovery is possible after deletion.
Zero data collection extends beyond documents to encompass user information. No email addresses, names, usage profiles, or behavioral data are gathered. Access keys provide functionality without identity linkage. The system cannot share user data with third parties because it possesses no user data to share.
No model training occurs using uploaded documents. Unlike platforms that claim broad rights to process user content for service improvement, EPH4 documents never contribute to AI training datasets. Proprietary information, confidential analysis, and sensitive materials remain exclusively under user control.
Encryption protects documents during the active session. Files are AES 256 encrypted during processing and transmission. The limited session duration further reduces exposure window compared to platforms that retain documents indefinitely.
This architecture makes EPH4 suitable for sensitive materials that users would not trust to cloud services with indefinite retention policies. Confidential financial data, privileged legal documents, proprietary research, and private business information can be analyzed without creating permanent copies in third-party systems.